CANADIAN IMMIGRATION UPDATES: Applicants to Master’s and Doctoral degrees are not affected by the recently announced cap on study permits. Read more

Building Resilience in Coastal Cities of Bangladesh: Impacts of Climate Change on Urban Utility Services
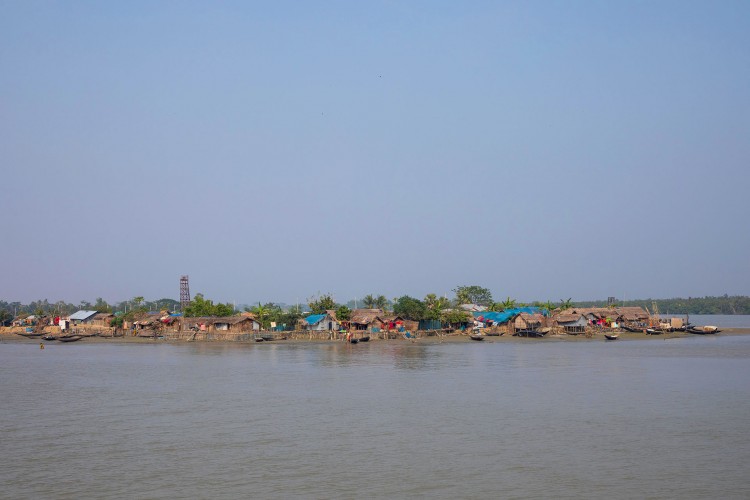

Mongla, Bagerhat, Bangladesh
CURE - Impacts of Climate Change on Urban Utility Services
Sarder Shafiqul Alam, Urban Climate Change Programme and Country Coordinator, ICCCAD (International Centre for Climate Change and Development)
Background
With the increased rate of climate change and urbanization, the coastal urban cities and towns of low-lying developing countries are receiving a large number of climate-induced migrants every day. Such phenomena put extreme pressure on the scarce urban resources and also affect the utility services available such as safe water supply and sanitation facilities. Urban utility services under the contest of climate change are, therefore, an important agenda that needs to be taken seriously by the researchers as well as the policymakers and governments.
Bangladesh is one of the most vulnerable countries under the context of climate change. The south-west region of Bangladesh has been chosen for the study as the area which is highly vulnerable to the cyclone with the surge, riverbank erosion, sea-level rise, flood, salinity intrusion, and waterlogging all of which are likely to be exacerbated by the impacts of climate change in the future. Water and sanitation of this region, however, are highly affected by the changing climate scenario.
Mongla Port Municipality has been affected by different types of climatic disasters such as cyclones with surges, increase salinity intrusion and river water tide levels, waterlogging, and increase of the temperature. Access to safe water, sanitation, and other facilities are very limited for most of the city people. The informal settlements of the city consist of mostly migrant community and they are economically poor. In recent years this group of poor people is increasing in the city on the other hand frequency and intensity of climatic disasters are also increasing. The current Mayor of the city is trying to build the city as one of the climate-resilient cities in the coastal region in Bangladesh. Due to a lack of research-based knowledge this resilient development activity is not effective for a long time. There is a lack of reliable data and updated information on the city population growth. Also, lack of climatic disasters vulnerability mapping and how the city people cope with disasters for getting access to water, sanitation, and livelihood income earnings are prominent.
Project focus
Research-based knowledge is required to understand the climate change-related disaster physical and social vulnerability at the city level. These knowledge products and information will be important resources to build long-term resilience. In turn, climate-resilient secondary cities and towns will attract new migrants instead of migrating to large cities which are already overpopulated. The Fall 2020 project will focus on the following themes:
- How vulnerable is the study region to the impacts of climate change?
- How do these vulnerabilities impact the sanitation and water services in the study area?
- How does the sanitation and other urban services, which are impacted by climate change, impact the quality of life and choice of migration of the urban poor?
- How can the situation can be improved to enhance the quality of utility services?
- What impact should this improved situation have on the choice of migration of the urban poor?